리눅스를 사용하다보면 다양한 이유로 다른 서버의 파일들을 가져와야 할 경우가 발생한다.
예를들어 서버 이전을 한다거나.. 새로운 프로그램 설치를 위해 다운로드를 받는다거나… 하는 여러 이유로
종종 사용하게 된다.. 나의 경우 호스팅 서버에서 다른 서버로 이전할 때 계정의 DB Dump와 소스 파일들을 tar로 묶고
바로 대상서버로 이전시키는 용도로 많이 사용한다.
FTP로 로컬로 받아서 다시 서버로 올려야하는 불편함이 줄어든다.
기본적인 사용법은 다음과 같다.
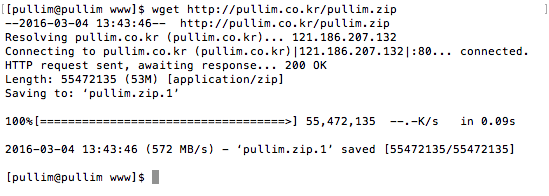
wget http://파일주소
위와같이 하면 현재 위치한 디렉터리로 파일이 받아진다. 완전 쉽죠잉~?
단순히 저렇게만 사용해서 편리함이 이루 말 할 수 없는데..
다양한 옵션들까지 제공한다.. 이 얼마나 친절한가!
다 설명할 순 없고 몇 가지 정말 유용한 옵션들을 적어본다.
1. 다운로드 속도 제한하기
서버를 운영하다보면 이용중인 회선에 따라 다르겠지만 대역폭 관리가 참 중요하다.
한 계정에서 큰 파일을 수시로 다운로드 하면서 서버 회선의 대역을 다 써버리면…?
다른 계정의 이용자들이 불편함을 겪는다.. 서버 응답이 느려지고 전송속도가 느려지니 답답할 따름…
wget으로 서버 이전할 때 별다른 옵션이 없으면 가능한 최대 속도로 전송을 하게 된다.
이럴 때 일정 속도로 다운로드를 제한하는 방법은 다음과 같다.
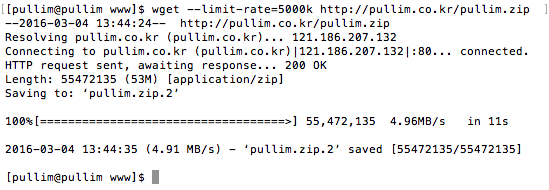
wget –limit-rate=5000k http://파일주소
위와같이 입력하고 엔터를 땅! 치면…
다운로드 속도는 5Mbps(=5000Kbps)로 제한되며..
해당 서버의 전체 대역 중 5Mbps만을 사용해서 데이터를 땡겨 올(전문용여죠 ㅎㅎ) 수 있는것이다.
10Mbps로 다운을 받으려면…?
옵션을 –limit-rate=10000k와 같이 입력하면 된다.
참 쉽죠잉~?
2. 백드라운드로 다운받기
wget으로 다운을 받으면 fore ground로 다운을 받으므로 다른 작업을 할 수 없다..
다른 커맨드 창으로 또 접속을 하거나 다운이 끝날 때 까지 기다려야 다른 작업을 할 수 있는 것이다.
이런 문제점을 해결하기 위해서 백그라운드로 다운로드할 수 있는 옵션이 있다.
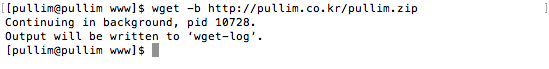
wget -b http://파일주소
위와같이 명령을 하면 백그라운드로 다운로드가 진행이 되고 다른 작업을 진행 할 수 있다.
백그라운드로 다운로드를 받는데.. 어느정도 다운이 받아지는지 궁금하다?
그럼 어떻게 해야할까요~?
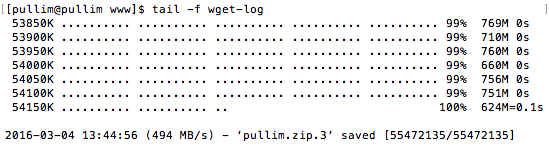
다음과 같이 입력하면 백그라운드로 다운로드중인 내역을 볼 수 있습니다.
tail -f wget-log
tail을 종료하려면~? Ctrl + C 를 누르면 됩니다.
3. 이어받기
파일을 다운로드 받다가 갑자기 오류 혹은 실수로 다운로드를 종료시켜버린 경우…?
걱정 마셔요~ 친절한 wget씨는 이어받기 옵션을 제공합니다.
사용법 또한 매~우 간단한데요^^
다음을 보실까요~?
wget -c http://파일주소
위와같이 입력해주시면 이어받기가 시작됩니다.
참 쉽죠~?
쉬운 옵션들이니까 외워두면 정말 유용합니다.
4. 다운로드 URL이 파라미터 형태일 때 정상적인 파일 받기
게시판 등에서 파일을 다운로드 할 때 주소가 http://www.pulli.me/download.php?id=1234
와 같을 경우 파일은 id=1234 그리고 파일은..? 내가 원하는 파일이 아니고 해당 스크립트가 실행된 결과값이 저장된다.
이럴 경우 정상적으로!! 원래 다운로드 받고자 한 파일을 받아오는 옵션이 있다.
다음과 같다.
wget -O http://kalcapt,net/download.php?id=1234
위와 같이 입력하면 원하던 파일이 정상적으로 다운로드 된다.
상황에 따라서 유용한 옵션들만 적어보았다..
기타 옵션이 궁금하다면.. wget -h 를 입력해서 매뉴얼을 보도록 하자.